Poultry Processing
On-Site Generated Electrolyzed Water
- SANITATION
- WATER DISINFECTION


Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water has been cleared by the FDA for no-rinse sanitation of poultry if generated from EcoloxTech systems. This includes carcasses, parts, trim, and organs. See FCN 1811 on the FDA website. Also see the letter from USDA Organic.

Per the FDA, poultry can be submersed in electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid in poultry chillers at concentrations up to 60 ppm when generated from EcoloxTech systems. No post-rinse is required. See FCN 1811 on the FDA website.

Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water is consistent with USDA organic labeling. Electrolyzed water is all natural, generated from food grade table salt, water, and electricity. See the letter from USDA Organic.

Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water is safe and non-irritant and can be used to help sanitize hands and feet prior to entering a facility.

Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water can be used to sanitize contact surfaces, equipment, floors and bathrooms.
On-Site and On-Demand
EcoloxTech systems are compact and easy to install. Systems are designed to generate Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water on-site and on-demand from an additive made yourself with just table salt and water.
What is Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water?
Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water is electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid (HOCl), a neutral-to-acidic electrolyzed water. HOCl has been studied for over 100 years and it is an undeniable fact that it is a more powerful oxidant than chlorine bleach. Only within the last 30 years have we been able to generate solutions of near 100% HOCl in such a stable form. HOCl kills bacteria, bacterial spores, and viruses 100 times more effectively than chlorine bleach.
How does it work?
Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water is a powerful oxidant (800 to 1000 mV) that can kill microbial pathogens immediately upon contact by damaging cell walls or inactivate the pathogen by entering and disrupting proteins, lipids, and DNA.
Has it been researched?

In the last 30 years we have collected over 300 published research articles supporting the use of Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water. Nearly every common bacterial pathogen has been studied such as E. coli, Salmonella, Listeria, Vibrio, Staphylococcus, MRSA, spore forming bacteria, and many common viruses (including Norovirus) and fungi. To learn more please visit our research page and search by microbe or industry to find applicable research.
What about regulation from FDA, USDA, and EPA?
We have pages dedicated to the regulation of electrolyzed water as it pertains to the FDA, USDA, and EPA. Please visit our pages for more information. In regards to healthcare sanitation, see our page for the CDC.
Meat and Processing Plant Sanitation
Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water (EOW), or electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid, has been approved by the FDA and USDA as an antimicrobial and as an ingredient that is safe and suitable on meat. Electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid can be used on meat directly for sanitation at concentrations as high as 60 ppm under Food Contact Notification (FCN) 1811. It is approved by the EPA for use on food contact surfaces at concentrations as high as 200 ppm. It is also approved for use in meat processing water at concentrations up to 5 ppm. Electrolyzed water (hypochlorous acid) has demonstrated in numerous studies to be highly effective for inactivating E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella enteritidis, and Listeria monocytogenes.
Direct Sanitation of Meat
The contamination of beef during the slaughter and processing of carcasses is a major risk for subsequent foodborne infection. Bacteria present on hides, hooves and other external surfaces of the cattle at the time of slaughter are potential sources of contamination of the carcass and subsequently of all derived beef products. The Code of Federal regulations acknowledges under 9 CFR 310.25 that fecal contamination of carcasses is the primary avenue for contamination by microbial pathogens. E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella enteritidis, and Listeria monocytogenes are common pathogens seen on meat and in meat processing facilities that cause foodborne illness. The CDC estimates that each year roughly 48 million people gets sick from a foodborne illness, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die. Current methods of direct meat sanitation involve hot water, steam, and organic acids such as lactic acid. Lactic acid is expensive for smaller processors and bacteria can develop resistance. Electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid is a powerful oxidant that is stable in solution. When saturating meat contaminated with microbial pathogens, hypochlorous acid quickly inactivates the pathogens by damaging their cell walls and disrupting their internal proteins, lipids, and DNA To learn more please visit our research page.
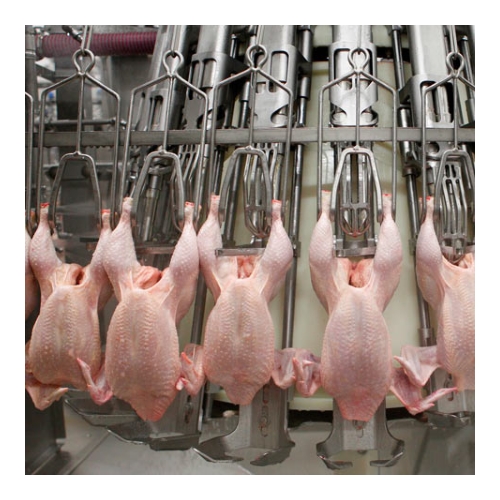

Sanitation in Poultry Chillers
The USDA has approved the use of electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid for use in poultry chillers at up to 50 ppm. Hypochlorous acid is considered a safe and suitable antimicrobial on poultry by the FDA and USDA. Electrolyzed water (hypochlorous acid) has demonstrated in numerous studies to be highly effective for inactivating E. coli O157:H7, Campylobacter, Salmonella enteritidis, and Listeria monocytogenes.
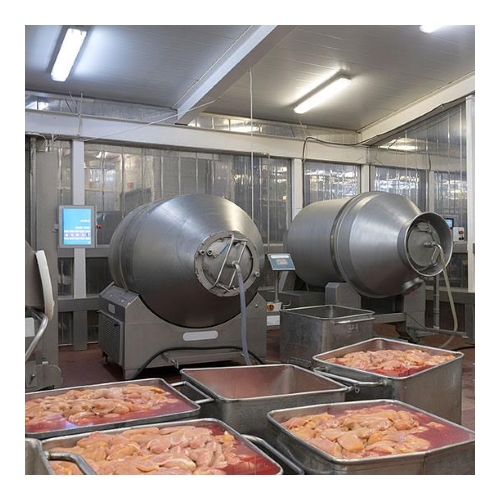

Pressure Spraying and Fogging
When cleaning and sanitizing contact surfaces, tools, equipment or large open areas, EOW can be appied via pressure sprayers or foggers. The active molecule in EOW is hypochlorous acid, a powerful oxidant that is stable in solution. Hypochlorous acid is approved by the EPA for use on food contact surfaces at concentrations as high as 200 ppm. EOW is highly effective at inactivating microbial pathogens when making contact in liquid form.
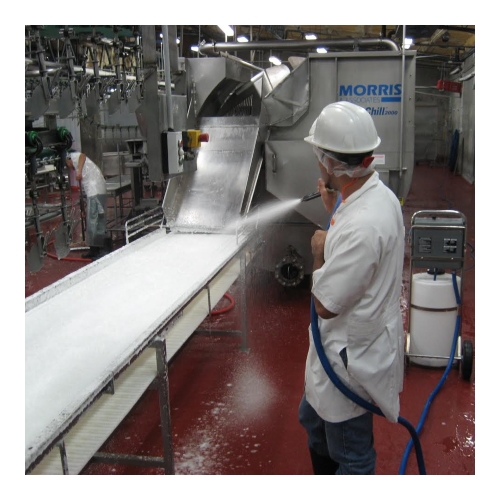

Eliminating Chemicals and Employee Safety
EcoloxTech electrolyzers eliminate the need for purchasing, transporting, storing, and preparing of toxic concentrated chemicals. Processing plants can switch to an environmentally friendly technology while saving time, space, and money. Electrolyzed water (hypochlorous acid) composed of hypochlorous acid is 100 times more effective than sodium hypochlorite yet requires no protective gear or safety equipment and is non-toxic, non-irritant, and eco-friendly.



Electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid is 100 times more effective at disinfecting process water than chlorine bleach and does not require a potable water post-rinse. See FCN 1811 on the FDA website. Also see the letter from USDA Organic.

EcoloxTech electrolyzers generate a powerful mixed oxidant solution that inactivate microbial pathogens by damaging their cell walls and disrupting their internal proteins, lipids, and DNA. To learn more please visit our research page
Sales/Quote Inquiries:
contact@ecoloxtechasian.com
+84 909 169 889
EcoloxTech Water Disinfection
The EcoloxTech 1200 Electrolyzer can disinfect water on-site and on-demand from just salt, water, and electricity.
How much water can it disinfect?
Each system can generate enough free available chlorine in the form of hypochlorous acid to disinfect 200 Liters of water per minute. The systems can be stacked to disinfect any volume of water
How does it work?
The EcoloxTech 1200 Electrolyzer generates a mixed oxidant solution primarily composed of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) but also other powerful oxidants such as ozone and chlorine dioxide. Hypochlorous acid is a powerful oxidant that is stable in solution that can kill microbial pathogens immediately upon contact by damaging cell walls and disrupting internal proteins, lipids, and DNA.
Has it been researched?

In the last 30 years we have collected over 300 published research articles supporting the use of Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water for disinfection. Nearly every common bacteria has been studied as well as viruses and fungi. To learn more please visit our research page and search by microbe to find applicable research.
What about EPA regulation?
Because electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid is a free chlorine molecule, it falls under the Safe Water Drinking Act (42 U.S.C. 300f et seq. 1974) which allows for a free chlorine concentration of up to 4 ppm.
Inactivating Microbial Contaminants
Water disinfection by electrochemical activation is not only more effective than conventional methods of water disinfection, but it is less expensive and environmentally friendly.
The conventional methods, which have seen extensive use over the last 100 years, include chlorine gas and chlorine solutions of sodium hypochlorite (bleach). Despite the vast amount of experience gained over the years, these methods have disadvantages, including the cost of the chemicals and the large investment required for protection and safety equipment.
Electrolyzed water composed of mixed oxidants and hypochlorous acid is 100 times more effective than sodium hypochlorite yet requires no protective gear or safety equipment and is non-toxic, non-irritant, and eco-friendly.

EcoloxTech electrolyzers eliminate the need for purchasing, transporting, storing, and preparing of toxic concentrated chemicals and can meet all the water disinfection needs of a processing plant by on-site generation. Fish and seafood processors can switch to an environmentally friendly technology while saving time, space, and money.
Electrolytically generated hypochlorous acid eliminates common microbial contaminants:
- Adenovirus
- Aeromonas
- Caliciviruses (including Norovirus)
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Clostridium botulinum
- Enterovirus (including polioviruses, coxsakieviruses, and echoviruses)
- Escherichia coli (O157)
- Helicobacter pylori
- Hepatitis A
- Legionella pneumophilia
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Mycobacterium avium
- Plesiomonas
- Salmonella enterica
- Shigella sonnei
- Vibrio species


